Calling APIs and Webhooks
Extend the Capabilities of Your Ask Steve Agents with APIs and Webhooks
Why Call an API or Webhook?
- This gives you the ability to call your own APIs that can do anything you want!
- As an example, you could configure an internal API that your Agent calls with an account number that it pulls from a page. Your API can use that account number to pull relevant data about that account from internal systems, directly make an LLM call with the new augmented data, and then pass the result back to your Agent.
- Or you could send the input to an LLM for processing, and then write it out to a Google Sheet or to Salesforce.
- Or you could proxy all requests so that you can log them, or filter any sensitive information out.
- You can do this with your own code running on a server somewhere, or with any visual workflow builder like n8n, Pipedream, Activepieces, Make, Zapier, Gumloop etc. that supports Webhooks.
- This enables you to do a lot more than just call an LLM!
Check out this Blog Post for a detailed walkthrough showing how to connect Ask Steve to a Make.com API
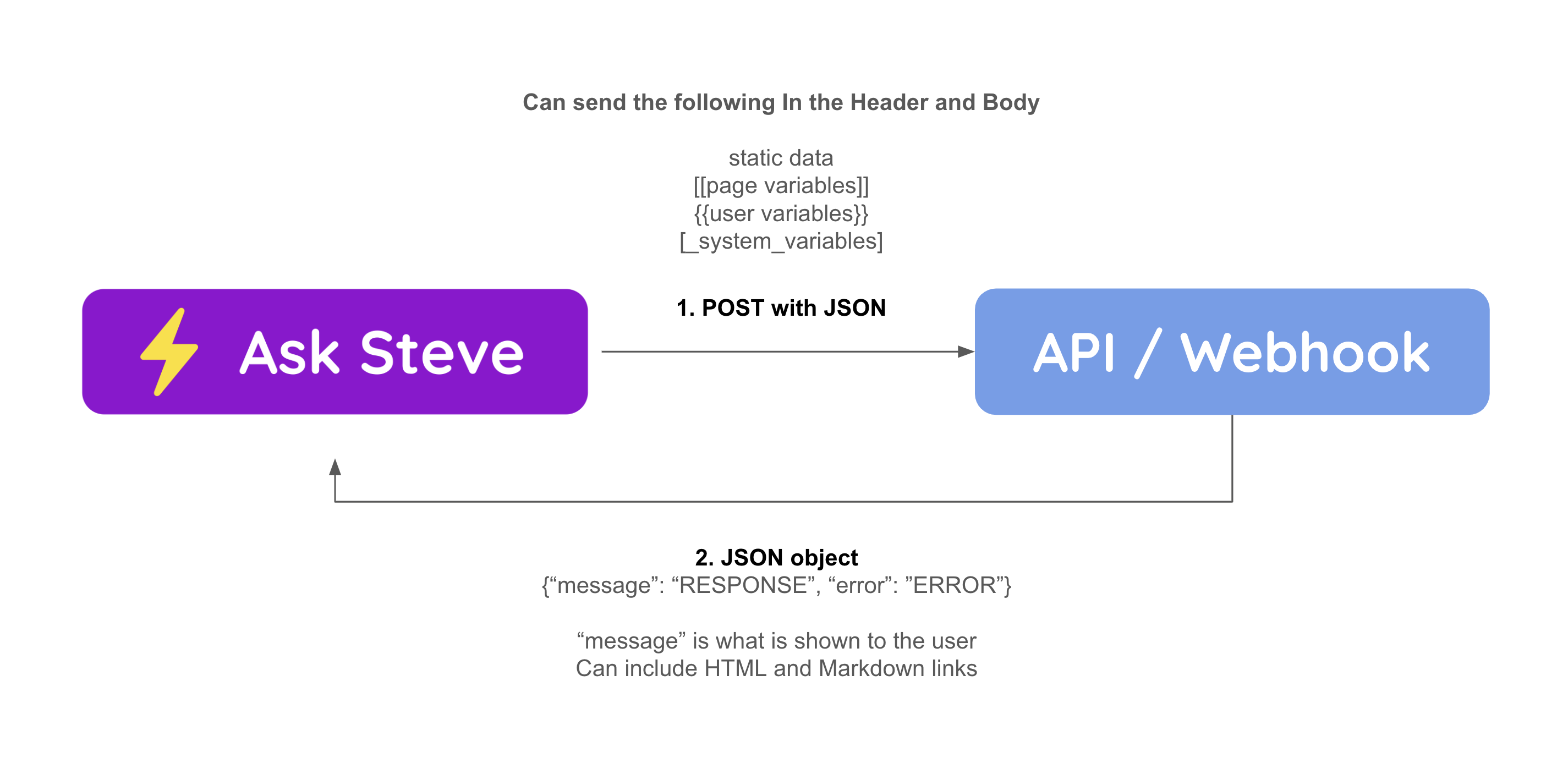
How to Call an API or Webhook
Ask Steve can interface with any API or Webhook on the back-end.
- To have an Agent call an API/Webhook instead of an LLM, open up the
Advanced Optionson the Agent and selectAPI / Webhookfrom theSend tolist. - API/Webhook Agents behave as follows:
- All requests are made via POST
- In the Agent configuration, the default header is to set the Content-Type to "application/json", but you can add anything else to the header that you need, including an API key or Authentication key.
- The body of the POST request automatically contains a property for every Page Variable, User Variable and System Variable. All other text in the "Instructions" area are ignored. If there are static variables in the body that you want to send, you can include them in the Agent configuration.
- The default behavior is that your API/Webhook should return an object with a "message" property (string) if it was successful, and an "error" property (string) if it was not. This is what will be shown to the user. You can change this if desired in the Agent configuration.
- You can include HTML and Markdown in what you return. URLs will be hyperlinked automatically.
Example Instructions: This Agent captures [[leads]] and sends them to a Webhook. [_url][_title]
The POST body will have the specified property "leads" with the selected text or current page. The system variables "_url" and "_title" will also be added. All other text is ignored and not sent to the API/Webhook.
Example Instructions: This Agent captures a [[headline]], [[author]] and [[article]] then asks the user for {{what do you want to do with this}} and then sends them to a Webhook
The POST body will have the three specified page variables, "headline", "author", "article" and the user-input variable "what do you want to do with this". All other text is ignored and not sent to the API/Webhook.
Inserting Variables into the Header or Body
You can insert any variable into the Header or Body. Any variables that don't have a placeholder in the Header or Body will be sent as top level variables in the Body as described above.
Example Header:
{
"Content-Type": "application/json"
"Authorization": "Bearer {{What is your API Key}}
}
This will take the User Variable "What is your API Key" and insert it into the Header.
Example Body:
{
"model": "mistral-moderation-latest",
"input": ["[[Text to Moderate]]"]
}
This will take the Page Variable "Text to Moderate" and insert it as a String in an Array as the value of the "input" key.